Sorting Rational and Irrational Numbers
Kiebala's Class
5 Followers
Grade Levels
6th - 8th
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS7.NS.A.1
CCSS8.NS.A.1
CCSS8.NS.A.2
Formats Included
- Flipchart File
Pages
4 pages
Kiebala's Class
5 Followers
Description
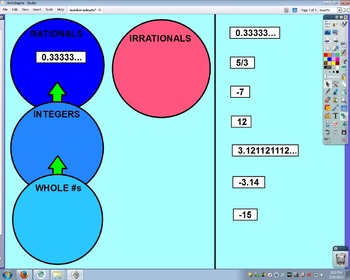
Students decide in which subset the numbers belong. By the end of the lesson, they take time to describe what the numbers in each subset look like.
Total Pages
4 pages
Answer Key
N/A
Teaching Duration
45 minutes
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS7.NS.A.1
Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram.
CCSS8.NS.A.1
Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number.
CCSS8.NS.A.2
Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., π²). For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of √2, show that √2 is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations.