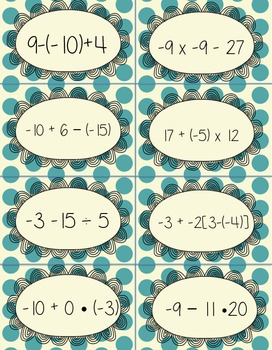
Order of Operations with Integers, Decimals, and Fractions War
STEM Savvy
187 Followers
Grade Levels
6th - 9th
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS7.NS.A.1b
CCSS7.NS.A.1d
CCSS7.NS.A.2a
CCSS6.EE.A.2c
Formats Included
- PDF
Pages
6 pages
STEM Savvy
187 Followers
What educators are saying
Great alternative way to introduce, teach, or remediate. Can be done individually, pairs or teams. Love games... engaging
Fantastic resource and it really allowed me to be able to have some quick problems that I could practice with the students.
Description
32 playing cards covering PEMDAS using Integers and positive and negative decimals and fractions. There are 16 cards with just integers, 8 with a combination of fractions and integers, and 8 with a combination of decimals and integers. Use it to review or as a math center.
Print on card stock and laminate. All operations are included.
Print on card stock and laminate. All operations are included.
Total Pages
6 pages
Answer Key
N/A
Teaching Duration
N/A
Last updated Sep 2nd, 2013
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS7.NS.A.1b
Understand 𝘱 + 𝘲 as the number located a distance |𝘲| from 𝘱, in the positive or negative direction depending on whether 𝘲 is positive or negative. Show that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0 (are additive inverses). Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts.
CCSS7.NS.A.1d
Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract rational numbers.
CCSS7.NS.A.2a
Understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distributive property, leading to products such as (–1)(–1) = 1 and the rules for multiplying signed numbers. Interpret products of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts.
CCSS6.EE.A.2c
Evaluate expressions at specific values of their variables. Include expressions that arise from formulas used in real-world problems. Perform arithmetic operations, including those involving whole-number exponents, in the conventional order when there are no parentheses to specify a particular order (Order of Operations). For example, use the formulas V = s³ and A = 6 s² to find the volume and surface area of a cube with sides of length s = 1/2.