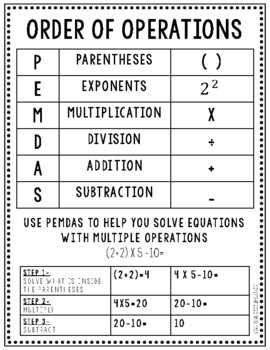
Order of Operations using PEMDAS Anchor Chart
Second Grade is Super
171 Followers
Grade Levels
3rd - 12th
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS3.OA.A.1
CCSS3.OA.D.8
CCSS4.OA.A.3
CCSS5.OA.A.1
CCSS5.OA.A.2
Formats Included
- PDF
Pages
1 page
Second Grade is Super
171 Followers
Description
When teaching order of operations, this anchor chart explains how the PEMDAS acronym can help you in determining which operation to solve for first. Hang up behind your small group area, on the board for whole group learning or give to your aid for small group instruction.
Total Pages
1 page
Answer Key
N/A
Teaching Duration
N/A
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS3.OA.A.1
Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7.
CCSS3.OA.D.8
Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.
CCSS4.OA.A.3
Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.
CCSS5.OA.A.1
Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols.
CCSS5.OA.A.2
Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. For example, express the calculation “add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2” as 2 × (8 + 7). Recognize that 3 × (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product.