Numbers in Base Ten Project- The Ultimate Family Vacation
- PDF
Description
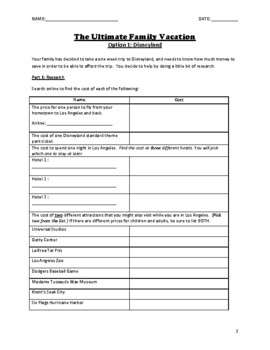
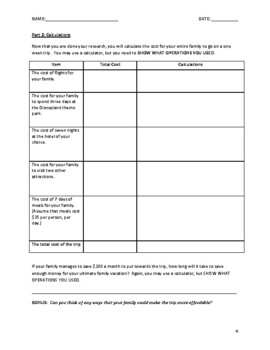
This is a differentiated project for helping students understand place value and decimals to the nearest hundredth. It also helps students build financial literacy. Students research and calculate the cost of a dream vacation- including flights, hotels, entrance fees, and meals. They then create a short presentation for the class.
There are four differentiated options.
-Students who have limited skills may simply research the cost of a trip to Disneyland.
-Students who have better skills may research the cost of a trip to any city in the world.
-Students requiring enrichment can conduct a cost comparison of a trip to either Disneyland and Disneyworld, or to two different cities anywhere in the world.
This project is ideal for grades 5 and 6; however, may also be a great enrichment opportunity for younger grades.