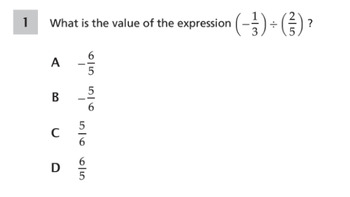NYS Math State Exam Practice Questions - Grade 7 - 2022-2023
Math with Mrs Meade
12 Followers
Grade Levels
7th
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS7.SP.A.1
CCSS7.SP.A.2
CCSS7.SP.B.3
CCSS7.SP.B.4
CCSS7.SP.C.5
Formats Included
- Google Forms™
Pages
21 questions
Math with Mrs Meade
12 Followers

Made for Google Drive™
This resource can be used by students on Google Drive or Google Classroom. To access this resource, you’ll need to allow TPT to add it to your Google Drive. See our FAQ and Privacy Policy for more information.
Description
This Google Form consists of 21 questions that come directly from the 2022-2023 NYS Math State Exam for Grade 7. Each question has only one answer, and all questions are worth 5 points except for #1 and #5. These two questions are straight calculator questions, therefore the points were split in half, in order to ensure a total of 100%.
There are several other Google Forms that also have NYS State Exam Questions form 2013 - 2018. Instead of a cumulative approach, these Google Forms focus on questions by skills. These Google Forms can be found in my TPT store as well.
Total Pages
21 questions
Answer Key
Included
Teaching Duration
N/A
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS7.SP.A.1
Understand that statistics can be used to gain information about a population by examining a sample of the population; generalizations about a population from a sample are valid only if the sample is representative of that population. Understand that random sampling tends to produce representative samples and support valid inferences.
CCSS7.SP.A.2
Use data from a random sample to draw inferences about a population with an unknown characteristic of interest. Generate multiple samples (or simulated samples) of the same size to gauge the variation in estimates or predictions. For example, estimate the mean word length in a book by randomly sampling words from the book; predict the winner of a school election based on randomly sampled survey data. Gauge how far off the estimate or prediction might be.
CCSS7.SP.B.3
Informally assess the degree of visual overlap of two numerical data distributions with similar variabilities, measuring the difference between the centers by expressing it as a multiple of a measure of variability. For example, the mean height of players on the basketball team is 10 cm greater than the mean height of players on the soccer team, about twice the variability (mean absolute deviation) on either team; on a dot plot, the separation between the two distributions of heights is noticeable.
CCSS7.SP.B.4
Use measures of center and measures of variability for numerical data from random samples to draw informal comparative inferences about two populations. For example, decide whether the words in a chapter of a seventh-grade science book are generally longer than the words in a chapter of a fourth-grade science book.
CCSS7.SP.C.5
Understand that the probability of a chance event is a number between 0 and 1 that expresses the likelihood of the event occurring. Larger numbers indicate greater likelihood. A probability near 0 indicates an unlikely event, a probability around 1/2 indicates an event that is neither unlikely nor likely, and a probability near 1 indicates a likely event.