Mystery Virus: Epidemic Epidemiology Case Study Simulation
- Zip
- Internet Activities
- Webquests
What educators are saying
Also included in
- Updated! This bundle includes everything you need to teach your students about viruses (including Covid-19) and the process of making vaccines.**Updated 3/14/21 - This bundle contains products that have been updated to reflect the most current CDC Guidance and information regarding new Covid-19 viruPrice $9.00Original Price $12.50Save $3.50
Description
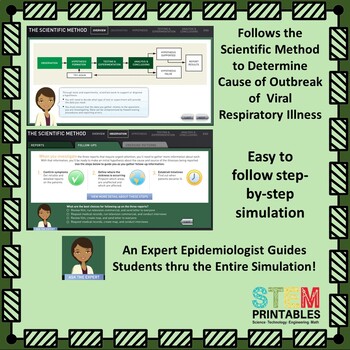
This highly engaging online simulation asks students to take on the role of a Public Health Director to determine the cause of a recent mystery deadly virus epidemic outbreak at a local High School and Senior Center.
In their role as Public Health Director, students are guided by an expert epidemiologist through the entire case study simulation which consists of:
- Studying medical reports and determining which ones to follow-up on
- Collecting information and identifying patterns of infection from patients
- Using the Scientific Method, develop & test a hypothesis to explain the outbreak.
- Evaluate epidemiological testing to determine what pathogen is causing the disease.
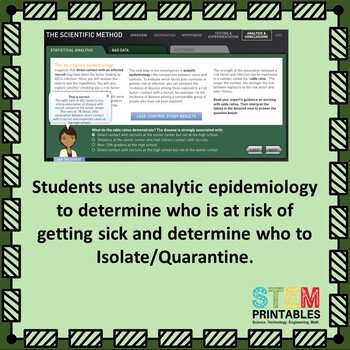
- Use epidemiology methods to determine the source and how the pathogen spreads.
- Make a recommendation on which patients should be isolated and quarantined.
Distance Learning: This simulation case study is appropriate for independent student work and should require minimal or no additional instructions from the teacher, The online simulation takes the student thru the entire process, step-by-step, with clear and concise directions from a virtual "expert epidemiologist".
Topics Covered
Scientific Method
Epidemiologist
Epidemic
Obtaining Medical records to confirm illness symptoms
Mapping locations of confirmed cases
Establish timelines and travel histories
Developing Hypothesis for what is causing illnesses and how it is spreading
Viral or Bacterial Culture
Blood Cultures
Rapid PCR Test
Blood Test for Antibodies
Case-Definition
Case-Control Study
Longitudinal Study
Analytic Epidemiology
Odds-Ratio
Tips for Customers
- Click the Green ★ to follow our store and get notifications of freebies and new products!
- Leave feedback to receive TpT credit for use on future purchases.
- Questions? Please contact us in the Product Q&A Section.
Terms of Use
All rights reserved by STEM Printables
This product is intended for use by the original purchaser only.
Sharing this product with others, distributing via any means, or posting online is strictly prohibited.
Failure to comply is a copyright infringement and a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA). Clipart and elements found in this PDF are copyrighted and cannot be extracted and used outside of this file without permission or license.