Multiplication Representations Pumpkin Activity
Mrs Hudson Teaches
2.4k Followers
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS3.OA.A.1
CCSS3.OA.B.5
CCSS3.OA.C.7
Formats Included
- PDF
Pages
20 pages
Mrs Hudson Teaches
2.4k Followers
What educators are saying
My students loved creating an art project connected to our multiplication unit. When we finished it was the ideal hallway display.
My class love this multiplication craftivity. It was a great way to ease into the concepts without overwhelming them.
Description
The perfect fall-themed activity to let your creativity juices flow and have your student practice the many different ways to represent multiplication! Grab some pumpkin seeds and let's get started!
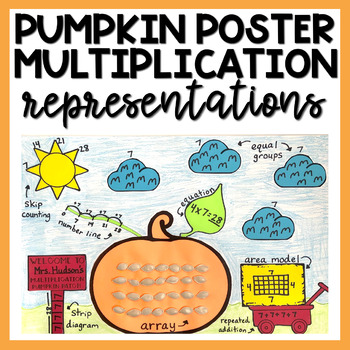
Strategies include:
- equal groups
- number lines
- skip counting
- area model
- repeated addition
- array
- strip diagram
- equation
Students will represent each of these strategies on a pumpkin patch themed template. Students will cut these out and assemble them on construction paper to create a pumpkin poster. Use pumpkin seeds to make the array, and print all these templates on colored paper for a bright POP! This is the perfect project to have on display in the hallway and/or for Open House or any other school activity.
Total Pages
20 pages
Answer Key
N/A
Teaching Duration
N/A
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS3.OA.A.1
Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7.
CCSS3.OA.B.5
Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.)
CCSS3.OA.C.7
Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division (e.g., knowing that 8 × 5 = 40, one knows 40 ÷ 5 = 8) or properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers.