Multiples Trains! Student-Generated Multiplication & Division Chart
- PDF
Also included in
- Are you a math teacher who works with students across multiple grade levels? This is your starter kit! With a focus on fluency and visual representation, this bundle contains something for every learner. Great for warm ups before lessons, small group sessions, or math centers to keep minds sharp. CoPrice $60.55Original Price $86.50Save $25.95
Description
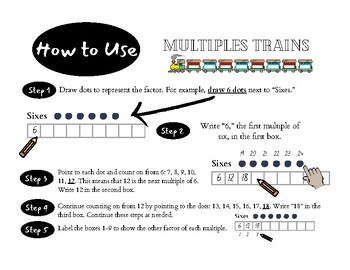
Multiples Trains is a tool for students to create their own reference sheet of factors and multiples that they can use to quickly and easily find any multiplication or division fact. This template is designed for students to use COUNTING ON in order to find all the multiples of a given number. To find all the multiples of six, for example, students simply draw 6 dots on the page. They write 6 as their first multiple in the train. Then, while pointing to each dot, they count on: 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12. Twelve is the next multiple in the train. Simply repeat these steps as needed.
Drawing arrays or equal groups, skip-counting, and repeated addition are multiplication strategies that often lead to errors. Furthermore, they are are time-consuming and frustrating strategies for students who need the facts FAST. Multiples Trains is a tool that eliminates this barrier to solving multiplication and division problems, while empowering students to solve for themselves instead of relying on a pre-made multiplication chart. Counting on by ones is the only prerequisite skill your students will need.