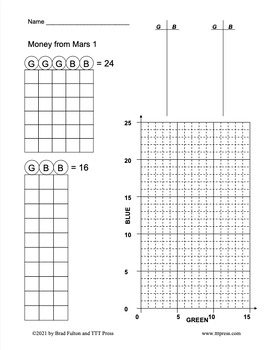
Money from Mars: Teaching Systems of Equations with Understanding
Teacher to Teacher Press
482 Followers
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS4.OA.A.2
CCSS4.OA.C.5
CCSS5.OA.A.2
CCSS5.OA.B.3
CCSS5.G.A.1
Formats Included
- PDF
Pages
36 pages
Teacher to Teacher Press
482 Followers
What educators are saying
Simple to use. I highly recommend watching Brad's video that explains how to use this resource in the classroom. They pair well together.
Description
This is an engaging and proven approach to teaching systems of equations. It has even been used with students in 4th & 5th grades successfully and is a great approach for students in pre-algebra classes, struggling algebra students, and even those in a traditional algebra program.
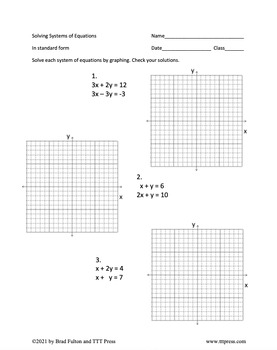
The multi-representational approach begins by integrating visual models with a guess-and-check strategy tied to t-tables and graphs fostering rich connections in conceptual understanding.
This then leads seamlessly into solving systems by elimination followed by substitution and graphing. The program has been used successfully by teachers throughout the nation at my workshops and trainings.
Total Pages
36 pages
Answer Key
Included
Teaching Duration
2 Weeks
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS4.OA.A.2
Multiply or divide to solve word problems involving multiplicative comparison, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem, distinguishing multiplicative comparison from additive comparison.
CCSS4.OA.C.5
Generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. Identify apparent features of the pattern that were not explicit in the rule itself. For example, given the rule “Add 3” and the starting number 1, generate terms in the resulting sequence and observe that the terms appear to alternate between odd and even numbers. Explain informally why the numbers will continue to alternate in this way.
CCSS5.OA.A.2
Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them. For example, express the calculation “add 8 and 7, then multiply by 2” as 2 × (8 + 7). Recognize that 3 × (18932 + 921) is three times as large as 18932 + 921, without having to calculate the indicated sum or product.
CCSS5.OA.B.3
Generate two numerical patterns using two given rules. Identify apparent relationships between corresponding terms. Form ordered pairs consisting of corresponding terms from the two patterns, and graph the ordered pairs on a coordinate plane. For example, given the rule “Add 3” and the starting number 0, and given the rule “Add 6” and the starting number 0, generate terms in the resulting sequences, and observe that the terms in one sequence are twice the corresponding terms in the other sequence. Explain informally why this is so.
CCSS5.G.A.1
Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the origin) arranged to coincide with the 0 on each line and a given point in the plane located by using an ordered pair of numbers, called its coordinates. Understand that the first number indicates how far to travel from the origin in the direction of one axis, and the second number indicates how far to travel in the direction of the second axis, with the convention that the names of the two axes and the coordinates correspond (e.g., 𝘹-axis and 𝘹-coordinate, 𝘺-axis and 𝘺-coordinate).