MHF4U - Grade 12 Advanced Functions - Full Course! - University Prep
Mr K's Science and Math Shop
91 Followers
Grade Levels
12th
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
CCSSHSF-IF.A.1
CCSSHSF-IF.A.2
CCSSHSF-IF.A.3
CCSSHSF-IF.B.4
CCSSHSF-IF.B.5
Formats Included
- Zip
Pages
Varies by Lesson
Mr K's Science and Math Shop
91 Followers
Description
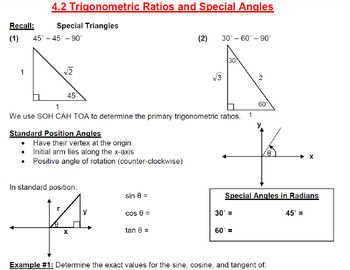
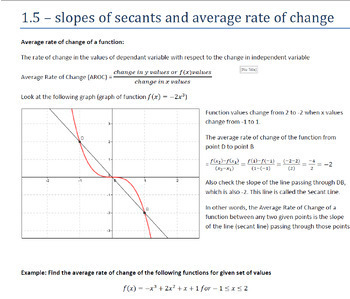
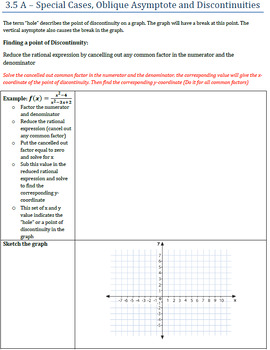
This is my complete course package for the Grade 12 Advanced Functions (MHF4U0) course following the Ontario Secondary Mathematics Curriculum. This package includes:
- A full set of PowerPoint, Smart Notebook, and Student PDF versions for every lesson of every unit in the course.
- A complete homework list that covers every lesson in the course. Each lesson concludes with appropriate homework sections from the textbook I typically use for this course (McGraw Hill Ryerson Advanced Functions 12)
- Appropriate unit tests/quizzes/assignments/inquiry problems for each chapter with answer keys.
- A complete culminating building task incorporating functions and construction.
- A complete final exam with associated review packages.
I hope you'll enjoy using this course package as much as I do!
If you have questions please don't hesitate to ask. I'm always happy to help.
Total Pages
Varies by Lesson
Answer Key
Included
Teaching Duration
1 hour
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSSHSF-IF.A.1
Understand that a function from one set (called the domain) to another set (called the range) assigns to each element of the domain exactly one element of the range. If 𝘧 is a function and 𝘹 is an element of its domain, then 𝘧(𝘹) denotes the output of 𝘧 corresponding to the input 𝘹. The graph of 𝘧 is the graph of the equation 𝘺 = 𝘧(𝘹).
CCSSHSF-IF.A.2
Use function notation, evaluate functions for inputs in their domains, and interpret statements that use function notation in terms of a context.
CCSSHSF-IF.A.3
Recognize that sequences are functions, sometimes defined recursively, whose domain is a subset of the integers. For example, the Fibonacci sequence is defined recursively by 𝘧(0) = 𝘧(1) = 1, 𝘧(𝘯+1) = 𝘧(𝘯) + 𝘧(𝘯-1) for 𝘯 greater than or equal to 1.
CCSSHSF-IF.B.4
For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities, and sketch graphs showing key features given a verbal description of the relationship.
CCSSHSF-IF.B.5
Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship it describes. For example, if the function 𝘩(𝘯) gives the number of person-hours it takes to assemble 𝘯 engines in a factory, then the positive integers would be an appropriate domain for the function.