Linearity & Functions | Quick Reference Sheets | 8th Grade Math Review | BUNDLE
- Zip
Products in this Bundle (5)
Also included in
- Thirty concepts are included in these 8th Grade Math Cheat Sheets. They can be used for students to review concepts they've already learned (great for end of year reviews), or as complete notes pages to help teach the concepts. These sheets are also helpful for parents and substitute teachers as a wPrice $22.35Original Price $32.35Save $10.00
Description
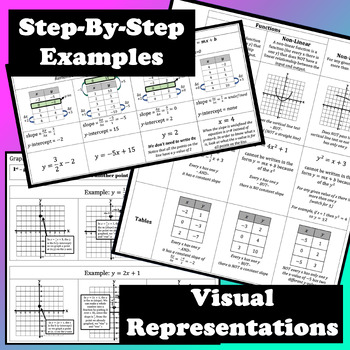
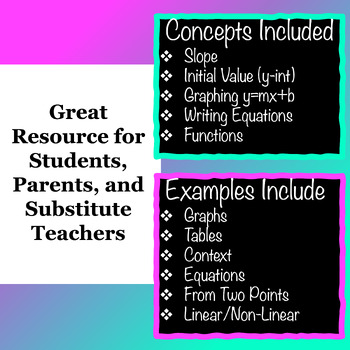
Great way to help students quickly review linearity and functions! These 8th Grade Math Cheat Sheets can be used for students to review concepts they've already learned (great for end of year reviews), or as complete notes pages to help teach the concepts. These sheets are also helpful for parents and substitute teachers as a way to refresh their memory of a concept so they're better able to help students.
More 8th Grade Math Reference Sheets available in my store as a larger BUNDLE (for a discounted priced) or separately:
30 Concepts (48 total pages) Included in This Larger Bundle:
- Absolute Value Equations (also includes guided notes & practice)
- Angle Sum Theorem
- Classifying Numbers
- Exponent Rules
- Expressions – Order of Operations & Evaluating
- Expressions – Simplifying (Distribute & Combine Like Terms)
- Exterior Angle Theorem
- Functions
- Graphing from Slope-Intercept Form
- Graphing Points on Coordinate Plane
- Inequalities – Solving & Graphing
- Initial Value (y-intercept)
- Line of Best Fit
- Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal
- Pythagorean Theorem
- Repeating Decimal to Fraction
- Scatter Plots
- Scientific Notation
- Similar Triangles (Angle-Angle Criterion)
- Slope
- Solving Equations
- Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination
- Solving Systems of Equations by Graphing
- Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution
- Square & Cube Roots
- Transformations
- Triangle Inequality Theorem
- Two Way Tables
- Volume (Cylinders, Cones, Spheres)
- Writing Linear Equations
Earning TPT Credits
After purchasing, remember to leave a review for this product in order to receive TPT credit! You can then use those credits toward other TPT purchases. Go to this link for more information about TPT Credits.