High School Astronomy Curriculum Outline
Miss Houston's Science Resources
10 Followers
Grade Levels
9th - 12th
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
NGSSHS-ESS1-6
NGSSHS-ESS1-4
NGSSHS-ESS1-3
NGSSHS-ESS1-5
NGSSHS-ESS1-1
Formats Included
- PDF
Pages
4 pages
Miss Houston's Science Resources
10 Followers
Description
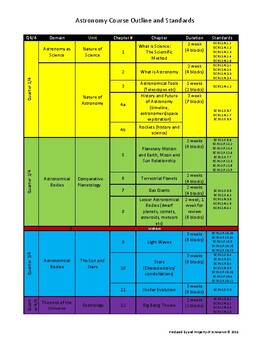
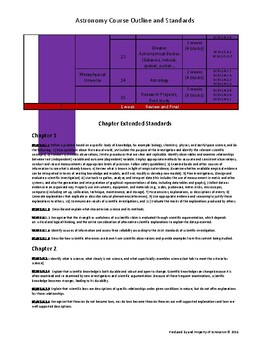
Developed independently as the only person in the Pinellas County School District to teach Astronomy Honors, this outline utilizes FL standards to create a year long pacing guide for a high school astronomy course. Content is organized into quarters, domains, units, chapters and estimated time by block schedule to help an educator organize their astronomy course. Each section is supported by FL state standards.
Total Pages
4 pages
Answer Key
N/A
Teaching Duration
1 Year
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
NGSSHS-ESS1-6
Apply scientific reasoning and evidence from ancient Earth materials, meteorites, and other planetary surfaces to construct an account of Earth’s formation and early history. Emphasis is on using available evidence within the solar system to reconstruct the early history of Earth, which formed along with the rest of the solar system 4.6 billion years ago. Examples of evidence include the absolute ages of ancient materials (obtained by radiometric dating of meteorites, moon rocks, and Earth’s oldest minerals), the sizes and compositions of solar system objects, and the impact cratering record of planetary surfaces.
NGSSHS-ESS1-4
Use mathematical or computational representations to predict the motion of orbiting objects in the solar system. Emphasis is on Newtonian gravitational laws governing orbital motions, which apply to human-made satellites as well as planets and moons. Mathematical representations for the gravitational attraction of bodies and Kepler’s Laws of orbital motions should not deal with more than two bodies, nor involve calculus.
NGSSHS-ESS1-3
Communicate scientific ideas about the way stars, over their life cycle, produce elements. Emphasis is on the way nucleosynthesis, and therefore the different elements created, varies as a function of the mass of a star and the stage of its lifetime. Details of the many different nucleosynthesis pathways for stars of differing masses are not assessed.
NGSSHS-ESS1-5
Evaluate evidence of the past and current movements of continental and oceanic crust and the theory of plate tectonics to explain the ages of crustal rocks. Emphasis is on the ability of plate tectonics to explain the ages of crustal rocks. Examples include evidence of the ages oceanic crust increasing with distance from mid-ocean ridges (a result of plate spreading) and the ages of North American continental crust decreasing with distance away from a central ancient core of the continental plate (a result of past plate interactions).
NGSSHS-ESS1-1
Develop a model based on evidence to illustrate the life span of the sun and the role of nuclear fusion in the sun’s core to release energy that eventually reaches Earth in the form of radiation. Emphasis is on the energy transfer mechanisms that allow energy from nuclear fusion in the sun’s core to reach Earth. Examples of evidence for the model include observations of the masses and lifetimes of other stars, as well as the ways that the sun’s radiation varies due to sudden solar flares (“space weather”), the 11-year sunspot cycle, and non-cyclic variations over centuries. Assessment does not include details of the atomic and sub-atomic processes involved with the sun’s nuclear fusion.