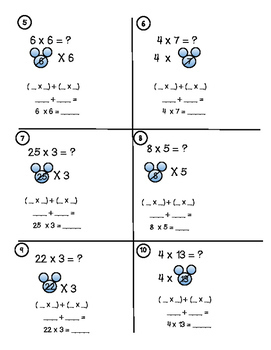Distributive Property of Multiplication - Fun Mouse Method
Ms Fox's Classroom
150 Followers
Grade Levels
3rd - 4th
Subjects
Standards
CCSS3.OA.B.5
Formats Included
- PDF
Pages
5 pages
Ms Fox's Classroom
150 Followers
What educators are saying
This was a great visual for a difficult concept. A new strategy for my students and made it much easier.
Some of my students have trouble with the commutative property, so I used this as an additional resource. This strategy isn't so friendly, as far as how the workbook sets it up, so this was a fun way to practice.
Also included in
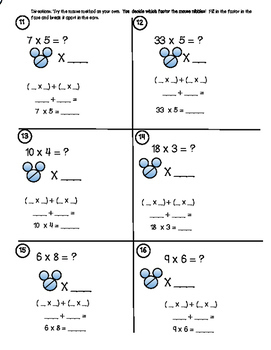
- The distributive property of multiplication state that multiplying two factors together gives the same result as breaking one factor into two addends, multiplying both addends with the remaining factor, then adding both products together.Why not make this fun and make a connection with mouse ears. LPrice $6.50Original Price $8.19Save $1.69
Description
The distributive property of multiplication state that multiplying two factors together gives the same result as breaking one factor into two addends, multiplying both addends with the remaining factor, then adding both products together.
Why not make this fun and make a connection with mouse ears. Learners "break" the addends by using the ears as a spot to put the two addends.
This step by step method walks learners through 16 scaffolded problems. I have also included a handout/anchor chart page and a page to laminate for small group instruction.
Could be used as whole group or in a small group setting.
Total Pages
5 pages
Answer Key
N/A
Teaching Duration
N/A
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS3.OA.B.5
Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.)