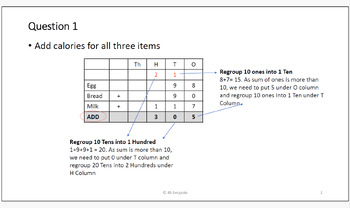
Counting Calories - Word Problems - Three digit addition & subtraction
8h bespoke
0 Followers
Grade Levels
3rd - 4th
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS3.NBT.A.1
CCSS3.NBT.A.2
CCSS4.NBT.A.2
CCSS4.NBT.B.4
CCSSMP1
Formats Included
- Zip
Pages
22 pages
8h bespoke
0 Followers
Description
Practical problems designed with underlying message to promote healthy eating amongst kids
Word problems with real life examples for kids to solve three digit addition & subtraction problems
Set includes word problems and detailed answer guide. Word problems can be used for Class/Home work or assessment purposes. Answer guide helps teacher go through step by step solutions in class or can be used for self learning
Total Pages
22 pages
Answer Key
Included with rubric
Teaching Duration
1 hour
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS3.NBT.A.1
Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100.
CCSS3.NBT.A.2
Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction.
CCSS4.NBT.A.2
Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons.
CCSS4.NBT.B.4
Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.
CCSSMP1
Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Mathematically proficient students start by explaining to themselves the meaning of a problem and looking for entry points to its solution. They analyze givens, constraints, relationships, and goals. They make conjectures about the form and meaning of the solution and plan a solution pathway rather than simply jumping into a solution attempt. They consider analogous problems, and try special cases and simpler forms of the original problem in order to gain insight into its solution. They monitor and evaluate their progress and change course if necessary. Older students might, depending on the context of the problem, transform algebraic expressions or change the viewing window on their graphing calculator to get the information they need. Mathematically proficient students can explain correspondences between equations, verbal descriptions, tables, and graphs or draw diagrams of important features and relationships, graph data, and search for regularity or trends. Younger students might rely on using concrete objects or pictures to help conceptualize and solve a problem. Mathematically proficient students check their answers to problems using a different method, and they continually ask themselves, "Does this make sense?" They can understand the approaches of others to solving complex problems and identify correspondences between different approaches.