The Science Suitcase
25 Followers
Grade Levels
Not Grade Specific
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS5.G.A.1
CCSS5.G.A.2
Formats Included
- PDF
Pages
5 pages
The Science Suitcase
25 Followers
Description
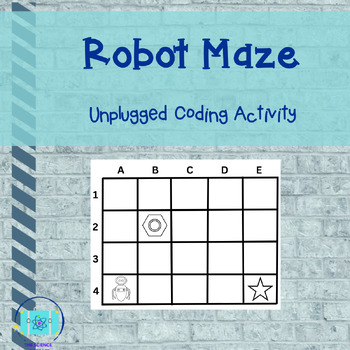
Are you introducing computer science to your elementary students? This maze activity teaches algorithms and the importance of step-by-step instructions.
Students help a character complete tasks on a grid, followed by writing a program.
Standards Alignment
CSTA
- K-2 1A-AP-08 Model daily processes by creating and following algorithms (sets of step-by-step instructions) to complete tasks.
- K-2 1A-AP-09 Develop programs with sequences and simple loops to express ideas or address a problem.
- 3-5 1B-AP-15 Test and debug (identify and fix errors) a program or algorithm to ensure it runs as intended.
Math
- 5.G.A Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems.
This free version includes black and white copies of the following:
- Three different grid sheets
- Program sheet
- Code cutouts
If you like this resource, be sure to check my paid versions which include:
- Color versions
- 15 plus different grid sheets
- Three levels of program sheets. ( pick up, jump, loops)
- Floor tiles
Total Pages
5 pages
Answer Key
N/A
Teaching Duration
N/A
Last updated 5 months ago
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS5.G.A.1
Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the origin) arranged to coincide with the 0 on each line and a given point in the plane located by using an ordered pair of numbers, called its coordinates. Understand that the first number indicates how far to travel from the origin in the direction of one axis, and the second number indicates how far to travel in the direction of the second axis, with the convention that the names of the two axes and the coordinates correspond (e.g., 𝘹-axis and 𝘹-coordinate, 𝘺-axis and 𝘺-coordinate).
CCSS5.G.A.2
Represent real world and mathematical problems by graphing points in the first quadrant of the coordinate plane, and interpret coordinate values of points in the context of the situation.