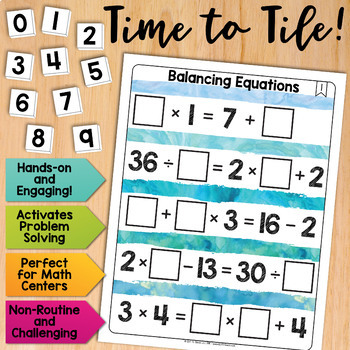
Balancing Equations Math Centers Math Tiles
- PDF
- Google Apps™

What educators are saying
Description
Time to Tile: Balancing Equations is a hands-on activity that takes students’ thinking beyond procedures and rote memorization. This engaging resource activates critical thinking and problem-solving skills, all while developing algebraic thinking. Students must place 10 number tiles (0-9) on the Time to Tile cards in order to correctly balance the equations.
This resource is now provided in printable and digital formats (Google Slides).
This resource includes:
•30 different Time to Tile cards
•An “Answer Recording Sheet,” where students can record their answers so they can be corrected later. This allows the resource to be used as a perfect independent or center activity.
•Answer keys
•Management and organization tips for successfully implementing Time to Tile in your classroom.
✏️For more math tile activities, click here.
More Time to Tile resources:
Time to Tile: Equivalent Fractions
Time to Tile: Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Time to Tile: Adding and Subtracting
Time to Tile: Order of Operations
Time to Tile: Multi-Digit Multiplication
Time to Tile: Area and Perimeter
Get all the latest Teacher Thrive news!
➜FOLLOW me on Teachers Pay Teachers!
➜FOLLOW me on TeacherThrive.com!
Please read: This is a nonrefundable digital download. Please read the description carefully and examine the preview file before purchasing.
© Copyright 2018 M. Tallman. All rights reserved. Permission is granted to copy pages specifically designed for student or teacher use by the original purchaser or licensee. This is intended to be used by one teacher unless additional licenses have been purchased. The reproduction of any other part of this product is strictly prohibited. Copying any part of this product and placing it on the Internet in any form (even a personal/classroom website) is strictly forbidden. Doing so makes it possible for an Internet search to make the document available on the Internet, free of charge, and is a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA).