Atomic & Nuclear Physics: Exploring the Building Blocks of Matter -
- PDF
Description
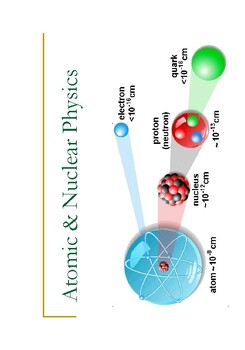
'Atomic & Nuclear Physics: Exploring the Building Blocks of Matter' provides information about atomic and nuclear physics. It begins by explaining how atoms are essential for life, as we inhale oxygen atoms and release carbon dioxide atoms through the process of respiration. The structure of an atom is described, with a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons, and electrons orbiting around the nucleus. The concept of energy levels and excited states of electrons is introduced, where electrons can absorb or release energy, leading to the emission or absorption of photons. Energy level diagrams are used to represent these transitions.
The document then discusses the application of energy levels and transitions in spectroscopy, which is a technique used to identify materials based on their emission spectra. Different elements have unique emission lines, allowing scientists to analyze the composition of atmospheres or celestial objects by studying the light emitted from them.
The topic then shifts to nuclear physics and radioactive decay. The notation used to represent radioactive isotopes is explained, with the mass number and atomic number denoted by "A" and "Z," respectively. Isotopes are described as variations of the same element with different masses due to the presence of extra neutrons. The concept of energy-mass equivalence, proposed by Albert Einstein, is mentioned, highlighting the significant amount of energy stored within mass.
The document further discusses mass defect, which refers to the difference in mass between the separated particles of a nucleus and the intact nucleus itself. The release of energy and particles from unstable nuclei is referred to as radioactivity and radioactive decay. Different types of radioactive decay, such as alpha decay, beta decay, positron decay, and gamma decay, are explained, along with their applications in various fields.
Specific applications of radioactive decay are mentioned, including the use of alpha particles in smoke detectors, beta decay in betavoltaics and neutrino discovery, positron emission in positron emission tomography (PET), and gamma rays in radiation therapy and imaging techniques.
The document briefly touches upon nuclear fusion, which is the process of combining atomic nuclei to form a heavier nucleus, and its potential applications in energy production. Nuclear fission, the splitting of atomic nuclei, is also discussed, particularly in the context of nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons.
Please note that the description provided is a summary of the content based on the given excerpts, and it may not cover all the details and topics included in the complete document.