4th Grade Math Doodle Pages Sketch Notes Guided Note-Taking Year-Long Bundle
- Various file types
What educators are saying
Products in this Bundle (72)
showing 1-5 of 72 products
Bonus
Description
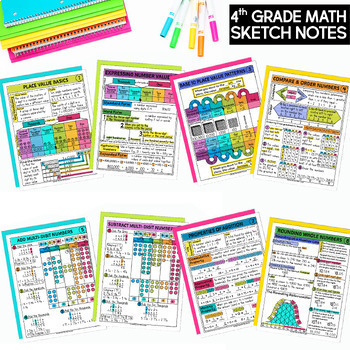
MATH SKETCH NOTES
These 4th-grade math sketch notes (AKA doodle pages) are a powerful learning and teaching tool. They cover essential math concepts and procedures for students in a visually appealing way. You can use this resource to supplement any math curriculum, and they are perfect for previewing/pre-teaching or reviewing/reinforcing.
These sketch pages are like mini anchor charts that your students actively create and can be referred to in the future.
72 SKILLS/CONCEPTS COVERED:
- Place Value Basics (Whole Numbers)
- Expressing Number Values (Whole Numbers- Standard Form, Word Form, Expanded Form)
- Base 10 Place Value Patterns
- Compare and Order (Whole Numbers)
- Add Multi-Digit Whole Numbers
- Subtract Multi-Digit Whole Numbers
- Properties of Addition
- Rounding Whole Numbers
- Estimation and Rounding with Whole Numbers
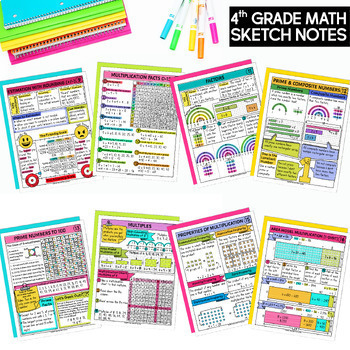
- Multiplication Facts and Strategies 0-12
- Factors
- Prime and Composite Numbers
- Prime Numbers to 100
- Finding Multiples
- Properties of Multiplication
- Area Model of Multiplication (1-Digit by Multi-Digit Factors)
- Area Model Multiplication 2-Digit Factor
- Partial Products Multiplication
- Multiplication Standard Algorithm 1-Digit by 3 and 4-Factors
- Multiplication Standard Algorithm 2-Digit Factors
- Estimating Products
- Distributive Property
- Multiply by Powers of 10
- Multiplicative Comparisons
- Long Division and Place Value
- Estimating Quotients
- Long Division and Area Model
- Partial Quotients with "Easy Multiples"
- Partial Quotients with Compatible Numbers
- Long Division Standard Algorithm
- Long Division and Interpreting Remainders
- Divide by Powers of 10
- Representing Fractions
- Composing and Decomposing Fractions
- Equivalent Fractions
- Benchmark Fractions
- Comparing to Benchmark Fractions
- Strategies for Comparing Fractions
- Simplifying Fractions
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions (Like Denominators)
- Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
- Add Mixed Numbers
- Subtract Mixed Numbers
- Multiply Fractions and Whole Numbers
- Fraction of a Set
- Decimals: Understanding Tenths
- Decimals: Understanding Hundredths
- Expressing Decimal Place Value (Word From and Expanded Form)
- Decimal Place Value Patterns
- Decimal Fractions
- More or Less: Decimal Numbers
- Order and Compare Decimal Numbers
- Adding Decimal Numbers (Tenths)
- Adding Decimal Numbers (Hundredths)
- Subtracting Decimal Numbers (Tenths & Hundredths)
- Lines, Line Segments, and Rays
- Understanding Angles (Acute, Right, Obtuse, and Straight)
- Measuring Angles with a Protractor
- Turns and Angle Measures
- Additive Angle Measures
- Classifying Triangles
- Classifying Quadrilaterals
- Lines of Symmetry
- Overview of Measurement (Customary and Metric)
- Converting Customary Units of Measurement
- Converting Metric Units of Measurement
- Elapsed Time
- Perimeter of Squares and Rectangles
- Area of Squares and Rectangles
- Perimeter and Area of Squares and Rectangles
- Missing Measurements of Rectangles
- Data Tables and Plot Graphs
EACH SKILL INCLUDES:
- Blank student note page (two sizes: 8.5 × 11 & composition notebook size for INBs)
- Detailed answer key
- Step-by-step PowerPoint
GUIDED NOTE-TAKING
Guiding your students through the note-taking process is so easy and requires almost zero preparation!
- PowerPoint: Each sketch note page comes with a step-by-step PowerPoint that you can use to guide your students as they complete their notes.
- Document Camera: Use a document camera to project a blank copy of the notes. Use the answer key provided to complete the note page in front of your students.
WHY SKETCH?
Sketch notes present your students with a meaningful and engaging activity they will love. Doodle note-taking activates verbal and visual modalities to capture concepts. The whole brain is absorbed in hearing, synthesizing, and retaining ideas. This high level of engagement helps students retain the content and leaves little room for distraction.
Get all the latest Teacher Thrive news!
➜FOLLOW me on Teachers Pay Teachers!
➜FOLLOW me on TeacherThrive.com!
Please read: This is a nonrefundable digital download. Please read the description carefully and examine the preview file before purchasing.
© Copyright 2018 M. Tallman. All rights reserved. Permission is granted to copy pages specifically designed for student or teacher use by the original purchaser or licensee. This is intended to be used by one teacher unless additional licenses have been purchased. The reproduction of any other part of this product is strictly prohibited. Copying any part of this product and placing it on the Internet in any form (even a personal/classroom website) is strictly forbidden. Doing so makes it possible for an Internet search to make the document available on the Internet, free of charge, and is a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA).